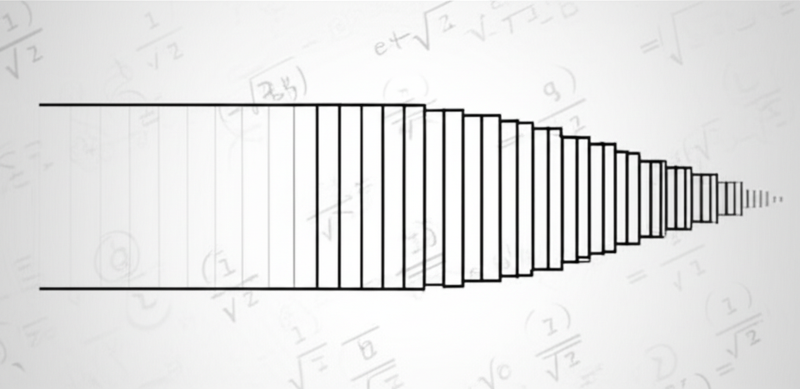
The Infinite Reach of Mathematical Series: A Philosophical Inquiry into Quantity and Logic
The concept of infinity, a notion that simultaneously captivates and confounds, finds one of its most profound expressions within the realm of mathematical series. Far from being mere abstract calculations, these sequences of numbers expose the very limits of our intuitive understanding of quantity, pushing us to re-evaluate what we mean by "sum" and "limit." This article delves into how mathematical series illuminate the philosophical challenges posed by infinity, demonstrating the exquisite interplay between mathematics, logic, and our quest to comprehend the boundless.
Unpacking Infinity: From Ancient Paradoxes to Modern Calculus
Our encounter with infinity is not a modern phenomenon. From the earliest philosophical inquiries, thinkers have grappled with the idea of the unending, the immeasurable. The Great Books of the Western World bear witness to this enduring fascination, particularly through the lens of ancient Greek thought.
Zeno's Paradoxes and the Problem of Infinite Divisibility
Consider Zeno of Elea, whose famous paradoxes, such as Achilles and the Tortoise, challenged the very notion of motion and quantity. Zeno argued that for Achilles to catch the tortoise, he must first cover half the distance, then half of the remaining distance, and so on, ad infinitum. This implies an infinite number of steps, each requiring a finite amount of time, leading to the seemingly illogical conclusion that Achilles could never start, let alone finish.
This early philosophical conundrum highlights a fundamental tension: how can an infinite number of parts contribute to a finite whole? It's a question of logic and our perception of quantity that mathematical series directly address. Aristotle, in his Physics, attempted to resolve such paradoxes by distinguishing between potential and actual infinity, suggesting that infinity exists not as a completed whole but as a process that can always be extended. This distinction proved foundational, providing a conceptual framework for later mathematical developments.
Defining Mathematical Series
At its core, a mathematical series is simply the sum of a sequence of numbers. A sequence is an ordered list, like (1, 2, 3, ...), while a series is the sum of those terms, like 1 + 2 + 3 + ... .
We categorize series primarily into two types:
- Finite Series: These have a limited number of terms and always result in a finite sum. For example, 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 = 10.
- Infinite Series: These continue indefinitely, summing an infinite number of terms. Herein lies the philosophical crux.
The intuitive assumption might be that an infinite number of positive terms must always sum to an infinite value. Yet, mathematics reveals a startling truth: many infinite series converge to a finite sum.
The Astonishing Convergence: Finite Sums from Infinite Terms
The most compelling philosophical insight offered by mathematical series comes from the phenomenon of convergence. Imagine a series where each term gets progressively smaller.
Example: The Geometric Series of Halves
Consider the series:
$$ \frac{1}{2} + \frac{1}{4} + \frac{1}{8} + \frac{1}{16} + \dots $$
Each term is half of the previous one, and the series continues infinitely. What is its sum?
| Term Number | Term Value | Partial Sum |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1/2 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 1/4 | 0.75 |
| 3 | 1/8 | 0.875 |
| 4 | 1/16 | 0.9375 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| As n approaches Infinity | Approaching 0 | Approaching 1 |
As we add more and more terms, the sum gets closer and closer to 1, but never actually exceeds it. In the language of mathematics, we say this infinite series converges to 1.
This is a profound realization. An infinite number of positive quantities can collectively amount to a finite, definite quantity. This challenges our everyday logic and intuition, which often struggles with the idea of an endless process yielding a conclusive result. It's a mathematical rebuttal to Zeno's paradox, offering a framework where an infinite number of steps can indeed lead to a finite destination.
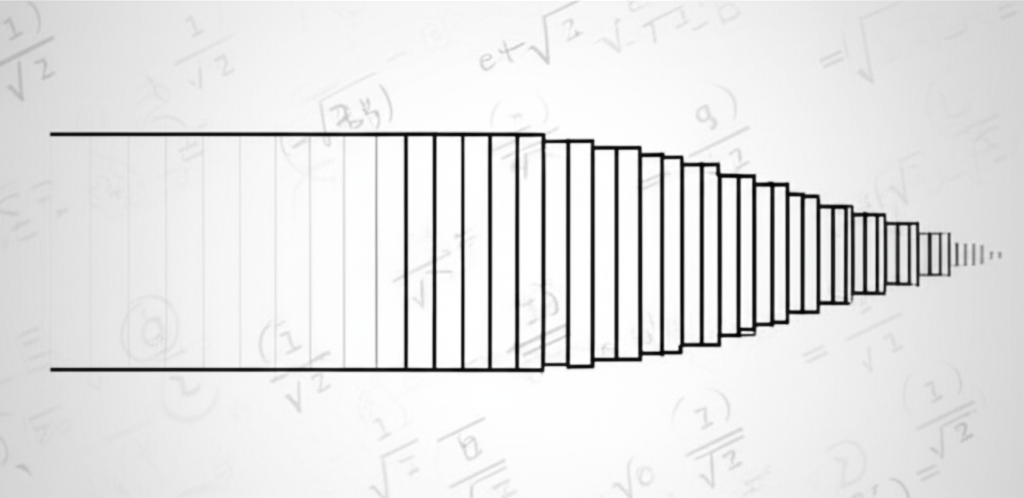
Divergent Series: When Infinity Remains Infinite
Not all infinite series converge. A divergent series is one whose sum approaches infinity (or oscillates without settling). For example, the harmonic series ($1 + \frac{1}{2} + \frac{1}{3} + \frac{1}{4} + \dots$) diverges, meaning its sum grows without bound, even though the individual terms approach zero. This contrast further highlights the nuanced nature of infinity in mathematics.
The Philosophical Implications for Logic and Quantity
The study of mathematical series, particularly convergent ones, forces us to refine our philosophical understanding of quantity and the limits of our logic.
- Rethinking "All": When we speak of the "sum" of an infinite series, we are not performing an endless addition in the conventional sense. Instead, we are describing the limit that the partial sums approach. This requires a leap of logic, moving beyond the finite operations we are accustomed to.
- The Power of Abstraction: Mathematics provides the abstract tools (like limits in calculus) to precisely define and manipulate infinity in ways that pure philosophical contemplation alone might find intractable. It transforms the vague notion of "endless" into a rigorously defined concept with tangible results.
- Beyond Intuition: The convergence of an infinite series demonstrates that logic can lead to conclusions that defy immediate intuition. It teaches us that our understanding of quantity must be supple enough to accommodate phenomena where the whole can be a finite entity composed of an infinite number of parts.
Conclusion: Infinity as a Bridge
The infinity of mathematical series serves as a powerful bridge between mathematics and philosophy. It is a testament to the human intellect's capacity to formalize and comprehend concepts that initially seem beyond grasp. By exploring how an infinite collection of quantities can yield a finite sum, we not only deepen our appreciation for the elegance of mathematics but also expand the very boundaries of our logic and understanding of the universe. The Great Books initiated this journey, and modern mathematics continues to provide new chapters in our ongoing dialogue with the infinite.
YouTube Video Suggestions:
-
📹 Related Video: KANT ON: What is Enlightenment?
Video by: The School of Life
💡 Want different videos? Search YouTube for: "Zeno's Paradoxes and the Concept of Infinity"
2. ## 📹 Related Video: PLATO ON: The Allegory of the Cave
Video by: The School of Life
💡 Want different videos? Search YouTube for: "What are Infinite Series? Calculus Explained"